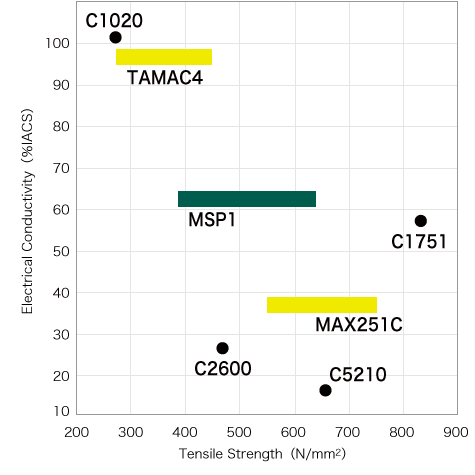
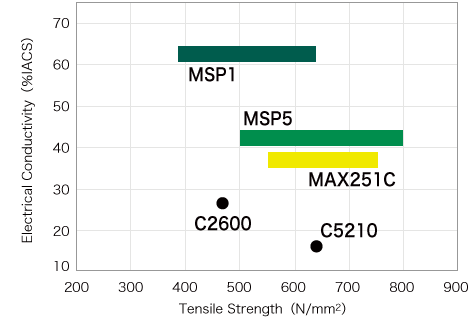
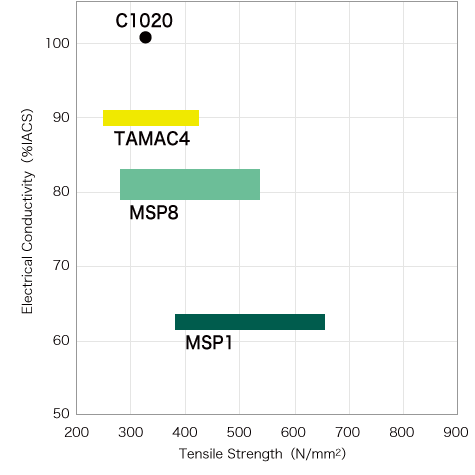
MSP Series of high-performance are solid solution strengthened Cu-Mg alloys. The lineup includes MSP1, which has been well received by customers and utilized for many years in electrical terminals for automotive applications, bus bars and relays; MSP5, which offers higher strength, bendability and low specific gravity making it ideal for use in compact-sized terminals; and MSP8, which offers superior electrical conductivity and excellent stress relaxation resistance that make it ideal for use in high-voltage, high-current applications such as bus bars and high-voltage terminals. In these ways, the series contributes to the advancement of electronics used in automobiles and other applications.
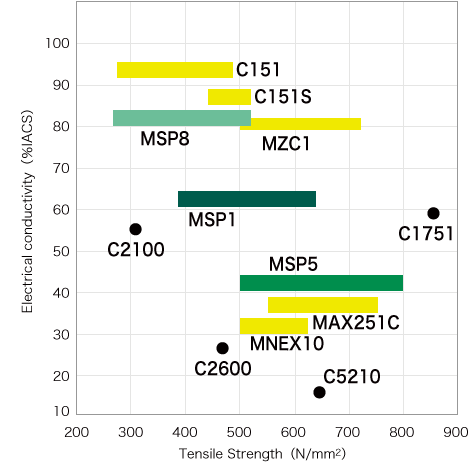
MSP1 has been widely used as a copper alloy for terminals, and its stable quality, characteristics, and supply network make it preferred by many users. It is our No. 1 global alloy, for which we have obtained CDA No. and established a supply network in 3 regions (North America, Europe, Asia). MSP1 is also adopted for use in high-voltage terminals in EVs and PHEVs.
MSP1 has been used for various parts such as connectors and busbars for automotive (ICE and xEV ) , moving contacts for relay , due to its excellent character, quality and supply network.
MSP1 is a global copper alloy with CDA No..
We can supply MSP1 to 3 regions(North America,Europe,Asia)
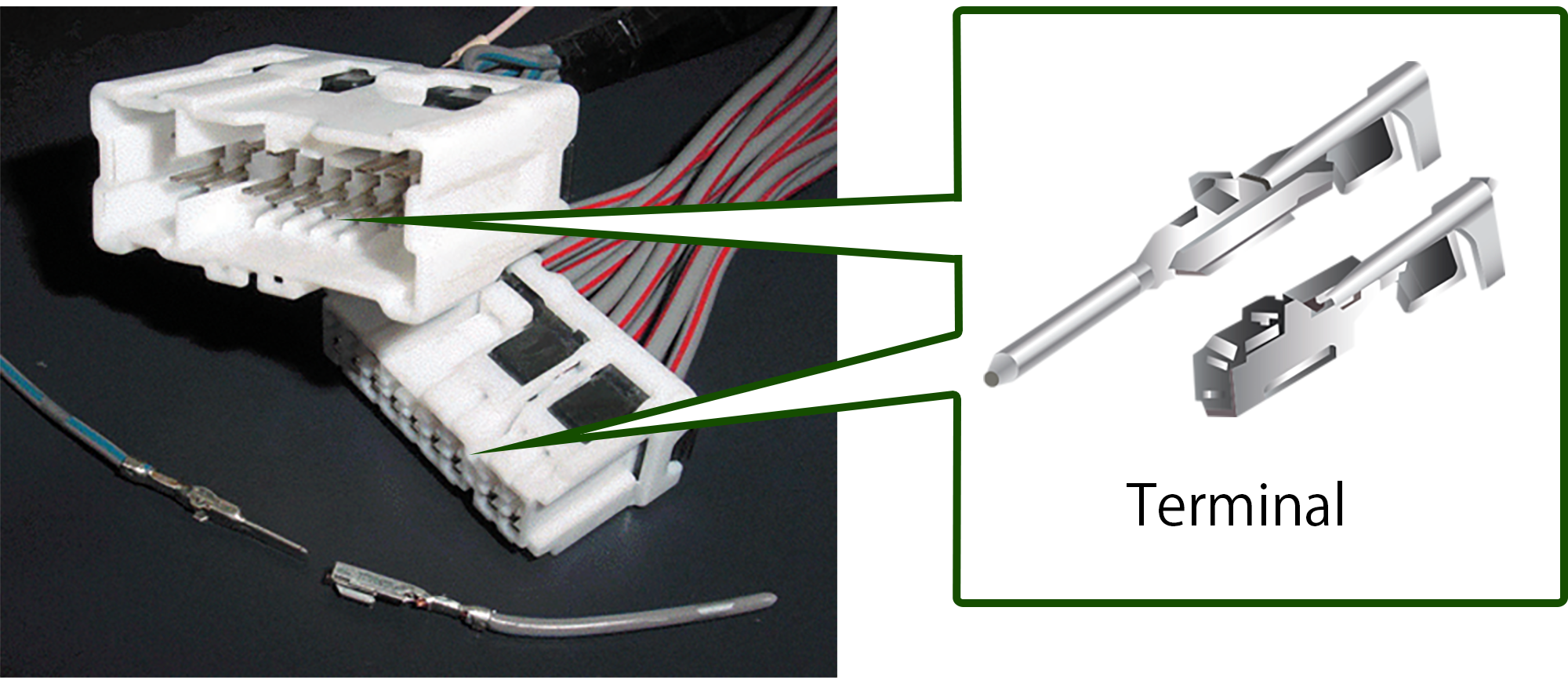
Terminals (for automotive applications), relays (moveable piece), spring materials for contacts, bus bars, breakers, battery terminals, fuse terminals, compact switches, electrical conductive parts in lithium ion batteries, junction boxes and relay boxes

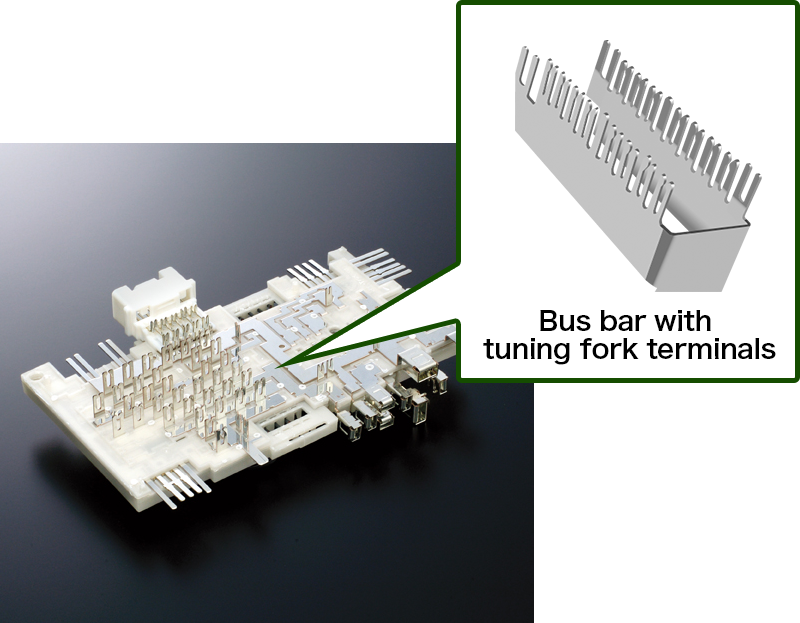

The chemical compositions of MSP1 are as follows.
(Weight %)
| Mg | P | Cu |
|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 0.005 | Rem.* |
The physical properties of MSP1 are as follows.
| Property | Representative Value |
|---|---|
| Specific Gravity (297K) |
8.8 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (×10-6/K : 293〜573 K) |
17.3 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/(m・K) : 293 K) |
264 |
| Volume Resistivity (µΩm : 293 K) |
0.027 |
| Electrical Conductivity (%IACS : 293 K) |
63 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (kN/mm2 : 293 K) |
125 |
The mechanical properties of MSP1 are as follows.
| Temper | Typical value | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4H | 1/2H | H | EH | SH | 1/4H | 1/2H | H | EH | |
| Tensile Strength (N/mm2) |
365〜450 | 420〜510 | 480〜570 | 540〜630 | 590min. | 399 | 459 | 530 | 585 |
| 0.2% Yield Strength (N/mm2) |
300〜410 | 370〜480 | 440〜550 | 490〜620 | 540min. | 328 | 432 | 494 | 560 |
| Elongation (%) |
15min. | 10min. | 7min. | 5min. | - | 25 | 15 | 11 | 8 |
| Elastic Limit*1 Kb0.1(N/mm2) |
- | - | - | - | - | (290) | (349) | (397) | (424) |
| Vickers Hardness*2 (HV) |
(90 〜140) |
(120 〜170) |
(150 〜190) |
(170 〜210) |
(180min.) | (126) | (144) | (162) | (178) |
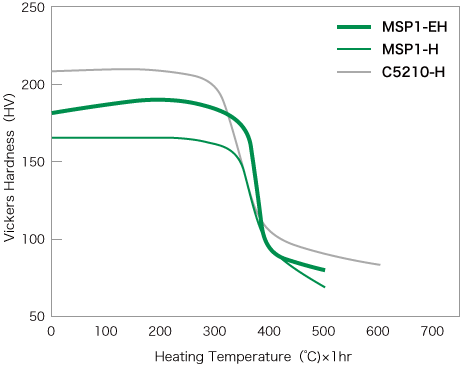
The Heat resistance of MSP1 is shown on the right.
MSP1 has sufficient Heat resistance for use as a terminal material, and as a spring material. It is especially suitable as an alternative to phosphor bronze.
The stress relaxation resistance of MSP1 are shown on the right.
MSP1 has excellent stress relaxation resistance among copper alloys and has extremely high reliability as a terminal material
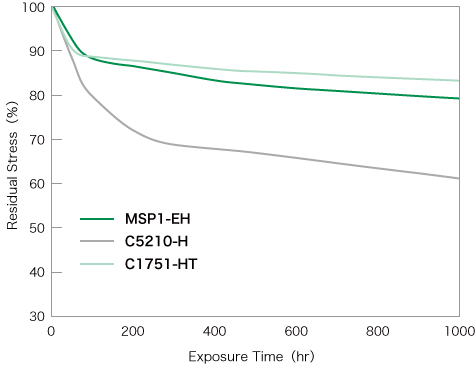
Exposure temperature: 150℃
Sampling direction: Parallel to the rolling direction
Bending stress: 80% of 0.2% yield strength
The bending workability of MSP1 is as follows.
MSP1 has not only an excellent balance of strength and conductivity, but also good bending workability, and can thus contribute to the miniaturization of various parts.
| Temper | Sampling direction (to the rolling direction) |
Bending Inside Radius (mm) R | Evaluation R/t |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.125 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 | |||
| 1/2H | 0°:(Good way) | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | 0.0 |
| 90°:(Bad way) | △ | △ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | 0.0 | |
| H | 0°:(Good way) | △ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | 0.0 |
| 90°:(Bad way) | ▲ | △ | △ | △ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | 0.3 | |
| EH | 0°:(Good way) | △ | △ | △ | △ | △ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | 0.0 |
| 90°:(Bad way) | ▲ | ▲ | ▲ | ▲ | ▲ | △ | △ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | 0.8 | |
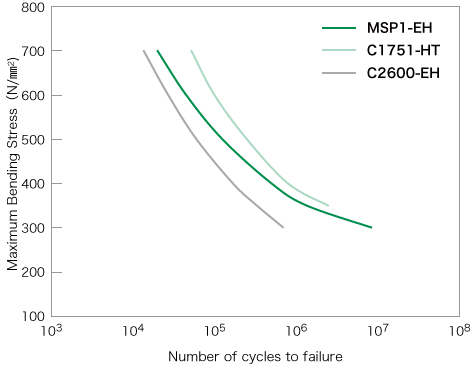
The fatigue characteristics of MSP1 are shown on the right.
MSP1 has excellent fatigue characteristics as a spring material, since it can be used numerous cycles before breaking.
MSP5 is the highest strength copper alloy in the MSP Series. Its combination of proper electrical conductivity, excellent stress relaxation resistance and bendability means that it is suitable for use as a terminal material for a diverse range of electronic and electrical devices where compact size is desired. In particular, it has been evaluated highly by customers as a copper alloy for compact-sized terminals for automotive applications. It is also suitable as an alternative to Corson alloys and phosphor bronze.
MSP5 offers high strength, electrical conductivity and stress relaxation resistance that are the same as (or superior to) our Corson type alloys, while at the same time offering excellent bending and blanking workability.
It is a high-strength copper alloy that is suitable for use as terminal and spring materials, including automobile 0.50 terminals and other compact terminals for automotive and other industries.
Terminals (for automobiles and other industries), relays (moveable piece), spring materials for contacts

The chemical compositions of MSP5 are as follows.
(Weight %)
| Mg | Cu |
|---|---|
| 1.6 | Rem.** |
The physical properties of MSP5 are as follows.
(Weight %)
| Property | Representative Value |
|---|---|
| Specific Gravity (297K) |
8.5 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (×10-6/K : 293〜573 K) |
18.2 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/(m・K) : 293 K) |
174 |
| Volume Resistivity (µΩm : 293 K) |
0.042 |
| Electrical Conductivity (%IACS : 293 K) |
43 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (kN/mm2: 293 K) |
115 |
The mechanical properties of MSP5 are as follows.
MSP5 has been designed with high strength to the perpendicular to the rolling direction, making it suitable for use in terminals for automotive applications.
(Weight %)
| Temper | Typical value(LD/TD) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2H | H | EH | SH | 1/2H 0.64mm thickness |
H 0.15mm thickness |
EH 0.15mm thickness |
SH 0.15mm thickness |
|
| Tensile Strength (N/mm2) |
485〜585 | 530〜630 | 575〜675 | 620〜720 | 543/565 | 593/645 | 625/695 | 677/780 |
| 0.2% Yield Strength (N/mm2) |
- | - | - | - | 507/512 | 543/592 | 585/647 | 636/735 |
| Elongation (%) |
5min. | 4min. | 3min. | 3min. | 11/16 | 9/14 | 7/12 | 7/10 |
| Elastic Limit*1 Kb0.1(N/mm2) |
- | - | - | - | (524) | (609) | (712) | (764) |
| Vickers Hardness*2 (HV) |
(145 〜205) |
(160 〜220) |
(175 〜235) |
(190 〜250) |
(178) | (193) | (203) | (219) |
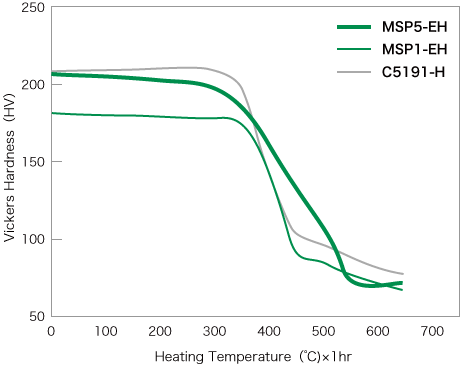
The Heat resistance of MSP5 is shown on the right.
MSP5 has sufficient Heat resistance for use as a terminal material, and as a spring material. It is also suitable as an alternative to phosphor bronze.
The stress relaxation resistance of MSP5 are shown on the right.
MSP5 offers stress relaxation resistance that are the same as (or superior to) our Corson alloys, making it suitable for use as a terminal material for automotive and other industries.
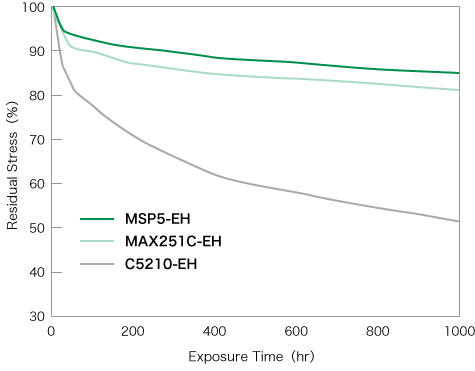
Exposure temperature: 150℃
Sampling direction: Perpendicular to the rolling direction
Bending stress: 80% of 0.2% yield strength
The bendability of MSP5 is as follows.
| Temper | Thickness (mm) |
Sampling direction (to the rolling direction) |
Bending Inside Radius (mm) R | Evaluation R/t |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.6 | ||||
| H | 0.15 | 0°:(Good way) | △ | △ | △ | △ | △ | ○ | ○ | 0.0 |
| 90°:(Bad way) | ▲ | △ | △ | △ | △ | △ | △ | 0.7 | ||
| EH | 0.15 | 0°:(Good way) | △ | △ | △ | △ | △ | ○ | ○ | 0.0 |
| 90°:(Bad way) | ▲ | ▲ | △ | △ | △ | △ | △ | 1.0 | ||
The cross section of automobile 0.50 terminal are shown on the right.
MSP5 offers excellent box-bending workability, making it possible to form into automobile 0.5 terminals and other compact terminals for automotive and other industries.
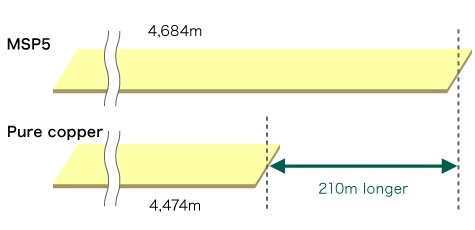
MSP5 has an approximately 5% lower specific gravity than pure copper and Corson alloys. This means that for the same weight, the length of the product is approximately 5% longer, and that many more terminals can be manufactured from the same weight of material.
MSP8 is the most suitable copper alloy for high-voltage and high-current applications in the MSP series. It offers high electrical conductivity (approximately 80% IACS) and excellent stress relaxation resistance, and is ideal for use as a material for bus bars and high-voltage terminals for next-generation automobiles.
It also has excellent press workability and high strength, enabling to form precise geometry.
MSP8 offers high electrical conductivity (approximately 80% IACS) and excellent stress relaxation resistance, and has excellent press workability and high strength. It is a high conductive copper alloy that is ideal for use in high-voltage terminals for automotive applications and high-current bus bars.
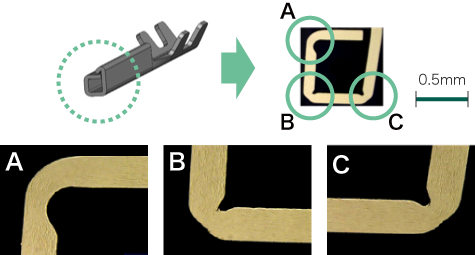
Terminals (for automotive applications), bus bars, charging connectors, relays (moveable piece), spring materials for contacts, electrical conductive parts in junction boxes, relay boxes




The chemical compositions of MSP8 are as follows.
(Weight %)
| Mg | P | Cu |
|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.002 | Rem.* |
The physical properties of MSP8 are as follows.
| Property | Representative Value |
|---|---|
| Specific Gravity (297K) |
8.9 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (×10-6/K : 293〜573 K) |
17.8 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/(m・K) : 293 K) |
340 |
| Volume Resistivity (µΩm : 293 K) |
0.021 |
| Electrical Conductivity (%IACS : 293 K) |
82 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (kN/mm2: 293 K) |
131 |
The mechanical properties of MSP8 are as follows.
| Temper | Typical value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4H | 1/2H | H | EH | 1/4H 3.0㎜ thickness |
1/2H 0.4㎜ thickness |
H 0.8㎜ thickness |
EH 0.64㎜ thickness |
|
| Tensile Strength (N/mm2) |
270〜370 | 320〜420 | 360〜460 | 420〜520 | 325 | 367 | 415 | 459 |
| 0.2% Yield Strength (N/mm2) |
- | - | - | - | 282 | 331 | 399 | 434 |
| Elongation (%) |
10min. | 6min. | 3min. | 2min. | 17 | 16 | 9 | 9 |
| Elastic Limit*1 Kb0.1(N/mm2) |
- | - | - | - | - | (334) | (357) | (384) |
| Vickers Hardness*2 (HV) |
(70 〜130) |
(85 〜145) |
(100 〜160) |
(110 〜170) |
(102) | (113) | (130) | (141) |
The Heat resistance of MSP8 is shown on the right.
MSP8 has sufficient Heat resistance for use as a terminal material, and as a spring material.
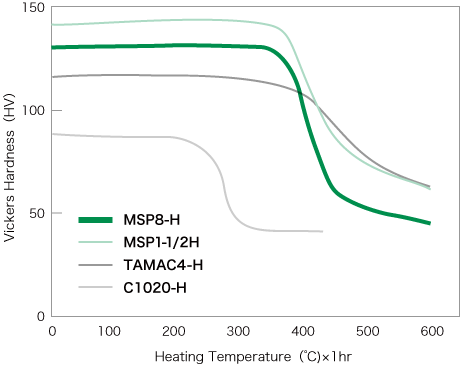
The stress relaxation resistance of MSP8 are shown on the right.
MSP8 has both high electrical conductivity and excellent stress relaxation resistance, making it appropriate for use in high-voltage terminals and bus bars.
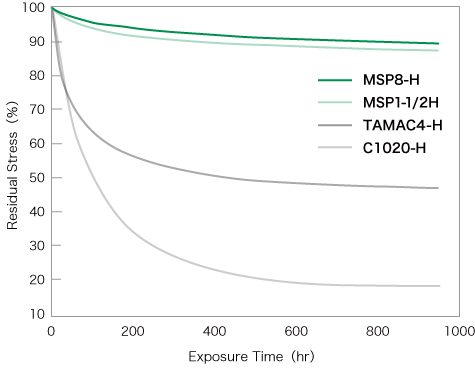
Exposure temperature: 150℃
Sampling direction: Parallel to the rolling direction
Bending stress: 80% of 0.2% yield strength
The bendability of MSP8 is as follows. MSP8 offers good bendability and is therefore suitable for high-voltage terminals and bus bars which require a high level of dimensional precision.
| Temper | Thickness (mm) |
Sampling direction (to the rolling direction) |
Bending Inside Radius (mm) R | Evaluation R/t |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 3.0 | ||||
| 1/2H | 0.4 | 0°:(Good way) | ▲ | △ | △ | △ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | 0.3 |
| 90°:(Bad way) | △ | △ | △ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | 0.0 | ||
| H | 0.64 | 0°:(Good way) | ▲ | ▲ | ▲ | △ | △ | △ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | 0.4 |
| 90°:(Bad way) | × | × | ▲ | ▲ | △ | △ | △ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | 0.6 | ||
| EH | 0.64 | 0°:(Good way) | ▲ | ▲ | ▲ | ▲ | △ | △ | △ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | 0.6 |
| 90°:(Bad way) | × | × | × | ▲ | ▲ | △ | △ | △ | ○ | ◎ | 0.9 | ||
The end face after blanking is sharp and uniform without coarse inclusions.
Boundary of shear surface and Fracture surface is linear without secondary shear surface.

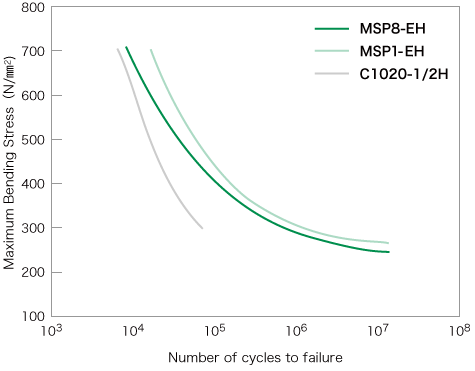
The fatigue characteristics of MSP8 are shown on the right.
MSP8 is suitable for use as a material for relays (moveable part) and springs, since it can be used numerous cycles before breaking.
TEL:+81-3-5252-4956
TEL:+81-72-233-9240